 Foreign minister Pekka Haavisto (L) hands over Finland’s NATO accession document to US secretary of state, Antony Blinken, as secretary-general Stoltenberg looks on, Brussels, 4 Apr 2023
Foreign minister Pekka Haavisto (L) hands over Finland’s NATO accession document to US secretary of state, Antony Blinken, as secretary-general Stoltenberg looks on, Brussels, 4 Apr 2023
The national flag of Finland was raised for the first time at the headquarters of the North Atlantic Treaty Organisation in Brussels on Tuesday, which also marked the 74th anniversary of the western alliance. It signifies for Finland a historic abandonment of its policy of neutrality.
Not even propagandistically, anyone can say Finland has encountered a security threat from Russia. This is an act of motiveless malignity toward Russia on the part of the NATO, which of course invariably carries the imprimatur of the US, while being projected to the world audience as a sovereign choice by Finland against the backdrop of Russia’s intervention in Ukraine.
Quintessentially, this can only be regarded as yet another move by the US, after the sabotage of the Nord Stream gas pipelines last September, with the deliberate intent to complicate Russia’s relations with Europe and render it intractable for the foreseeable future.
On the other hand, suffice it to say, this will also make Europe’s security landscape landscape even more precarious and make it even more dependent on the US as the provider of security. The general expectation is that Sweden’s accession to NATO will now follow, possibly in time for the alliance’s summit in Vilnius in July.
In effect, the US has ensured that the core issue behind the standoff between Russia and the West — viz., the expansion of the NATO to Russia’s borders — is a fait accompli no matter the failure of its proxy war in Ukraine against Russia.
Responding to the development, Kremlin spokesman Dmitry Peskov warned on Tuesday that Finland’s NATO membership will force Russia “to take countermeasures to ensure our own tactical and strategic security,” as Helsinki’s military alignment is an “escalation of the situation” and an “encroachment on Russia’s security.”
On April 4, the Russian Foreign Ministry stated that Moscow “will be forced to take retaliatory measures of both military-technical and other nature in order to stop threats to our national security.”
Finland’s NATO membership would extend NATO’s frontline with Russia by 1,300 kilometers (length of border Finland shares with Russia), which will put more pressure on Russia’s northwestern regions. Don’t be surprised if NATO missiles are deployed to Finland at some point, leaving Russia no option but to deploy its nuclear weapons close to the Baltic region and Scandinavia.
Suffice to say, the military confrontation between NATO and Russia is set to deteriorate further and the possibility of a nuclear conflict is on the rise. It is hard to see Russia failing to preserve its second strike capability at any cost or prevent the US from gaining nuclear superiority, and maintain the global strategic balance.
The focus will be on the upgrade of defensive nuclear capabilities rather than on conventional forces, compelling Russia to demonstrate its nuclear strength. Russia has already front-loaded its deterrent by deploying tactical nuclear weapons in Belarus in response to the UK’s irresponsible decision to provide depleted uranium munition to Ukraine. It is all but certain that Russia will also double down in the Ukraine conflict.
Meanwhile, the US has for long deployed tactical nuclear weapons in European countries, including Belgium, Germany, Italy, the Netherlands and Turkey, which means the US has long deployed its tactical nuclear weapons at Russia’s doorstep, posing a significant threat to Russia’s national security. Russia’s deployment in Belarus is aimed at deterring the US’ potential provocations, anticipating what is about to happen.
Belarus’ geographical location is such that if Russian tactical nuclear weapons are deployed there, it will have a huge strategic deterrent effect on several NATO countries such Poland, Germany, the Baltic states and even the Nordic countries. A vicious cycle is developing, escalating the nuclear arms race and ultimately developing into a doomsday situation that no one wants to see.
The big picture is that knowing fully well that the situation could become extremely dangerous, the US is nonetheless relentlessly piling pressure on Russia with the objective of perpetuating its hegemonic system. Ronald Reagan’s strategy to use extreme pressure tactic to weaken the former Soviet Union and ultimately drag it down, is once again at work.
In immediate terms, all this would have negative consequences for the conflict in Ukraine. It is plain to see that Washington no longer seeks peace in Ukraine. In the Biden Administration’s strategic calculus, if Russia wins in Ukraine, it means NATO loses, which would permanently damage the US’ transatlantic leadership and global hegemony — simply unthinkable for the Washington establishment.
Without doubt, the US-NATO move to persuade Finland (and Sweden) to become NATO members also has a dimension in terms of geoeconomics. The alliance’s secretary-general Jens Stoltenberg recently stated, “if Finland and Sweden join the alliance, NATO will have more opportunities to control the situation in the Far North.” He explained that “both of these countries have modern armed forces that are able to operate precisely in the harsh conditions of the Far North.”
The US hopes that the “expertise” to operate in the Arctic and sub-Arctic conditions that Sweden and Finland can bring into the alliance is invaluable as a potential game changer when a grim struggle is unfolding for the control of the vast mineral resources that lie in the Far North, where Russia has stolen a march so far.
As polar ice melts at unprecedented speed in the Arctic, the world’s biggest players are eyeing the region as a new “no man’s land” that is up for grabs. Some recent reports have mentioned that moves are afoot for the integration of the air forces of four Nordic countries — Denmark, Norway, Finland and Sweden — undertaken with an undisguised anti-Russian orientation.
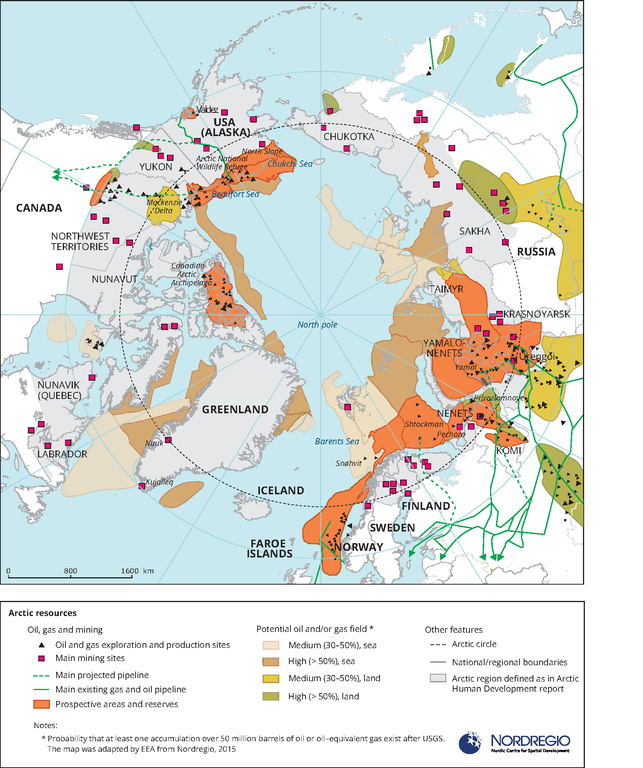 Arctic Resources
Arctic Resources
In military terms, Russia is being forced into sustaining the heavy financial burden of a 360 degree appraisal of its national security agenda. Russia has no alliance system supplementing its military resources. In an important announcement in February, paying heed to the straws in the wind, the Kremlin removed from its Arctic policy all mentions of the so-called Arctic Council, stressing the need to prioritise Russian Arctic interests, and striving for greater self-reliance for its Arctic industrial projects.
The revised Arctic policy calls for the “development of relations with foreign states on a bilateral basis,… taking into account the national interests of the Russian Federation in the Arctic.” This came days after a US state department official stated that cooperation with Russia in the Arctic was now virtually impossible.
